Technical Note
ZERO DISCHARGE SOLUTION FOR DISTILLERY EFFLUENT
Distillery effluent treatment has undergone phenomenal changes
in the wake of more and more stringent conditions imposed by
controlling agencies and rising public pressures. Wherein Zero Discharge
is an accepted concept, different versions put forward by different
technologies have not only created more confusion in the matter, but also
have proven to be exorbitant in their cost’s structures and very difficult
for practical working.
A viable alternative, which not only fulfills the
stipulations of controlling agencies, but also highly cost effective for the
parenting industry with a good payback potential is worked out and brief
details are given herewith.
PRIMARY TREATMENT
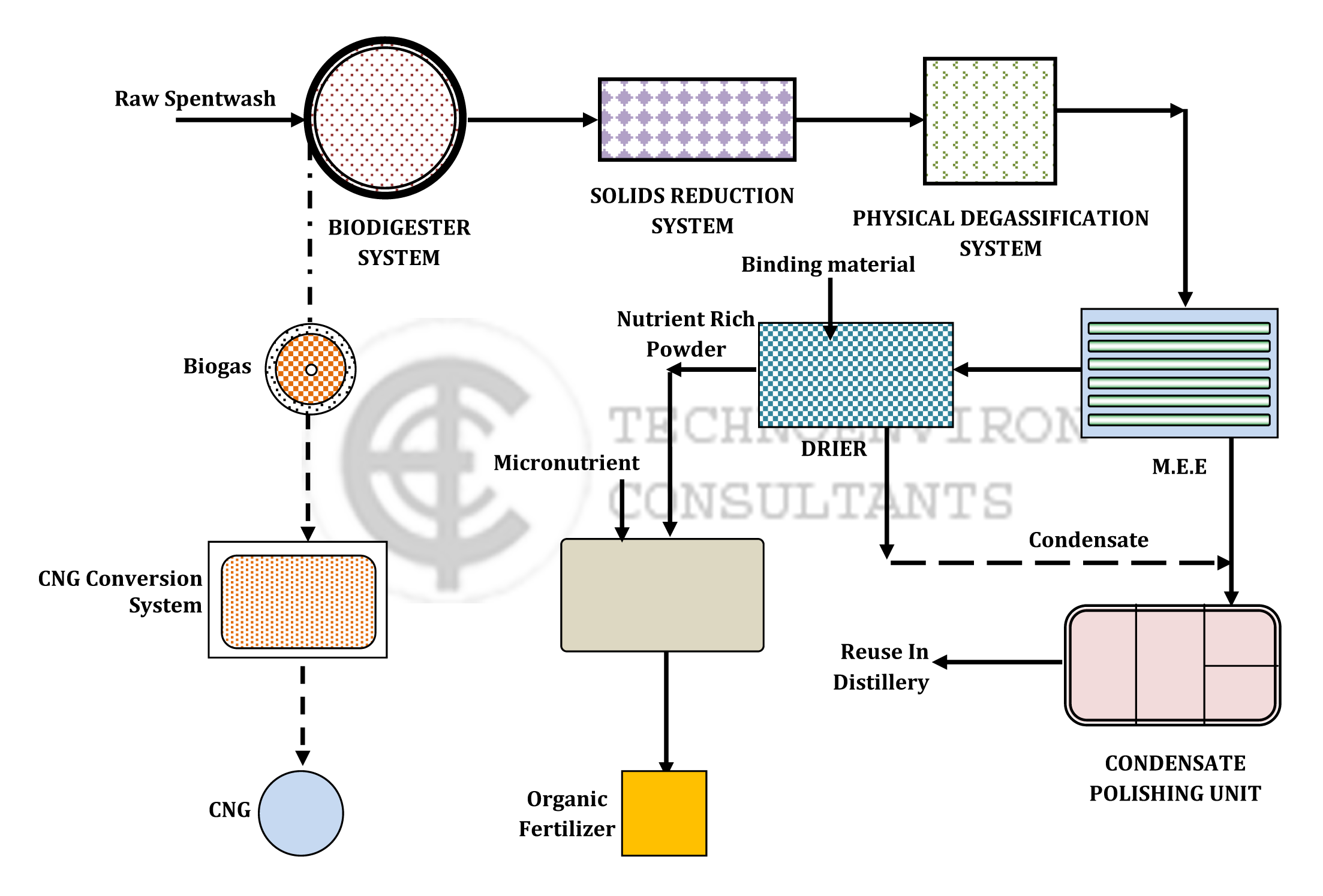
The technology of Bio-digester as a primary treatment is well established as the viable technology for Spentwash treatment and majority of distillery industry has already adopted the same. Apart from reduction in organic matter concentrations by over 75%, it culminates in biogas, which satisfies almost 90% of the steam requirement of the parent industry.
PRETREATMENT OF BIODIGESTED SPENTWASH FOR SOLIDS AND GASES REMOVAL
The volume of spent wash of about 8 – 10 lit/lit alcohol is required to be reduced in a Multi Effect Evaporator. This however posed two problems in practical projects
- Solids in the effluent
- Entrapped gases in the effluent
1. Solids in the effluent
There is a tendency to operate the biodigesters with higher biomass / solids concentration as an offset to variation in effluent conditions. This has resulted in heavy overflow of solids from the digester outlet. Again, the traditional technology of lamella clarifiers employed for reduction of the solids has proved to be non-effective. This was posing little problem when this effluent was directly taken to composting. However, as an inlet to RO / MEE, this becomes a real problem issue for working of these systems. We propose to provide a treatment structure for these solids concentration reduction, so that the volume reduction equipments function with their desired efficiency.
2. Entrapped Gases
Degasification for bio-digested effluent. The
normal degasser application is hardly efficient to carry out the
degasification of biodigested effluent, due to its unscientific &
inadequate design. This has led to severe problems in further
equipments like R.O. / M.E.E. and the main observation is heavy
foaming, limiting the equipment efficiency. Providing a heavy duty
thermal degasification ahead of these equipments was the only
solution thought of. A practical solution of physical degasification in
the optimum designed reactor removes majority of this entrainment
& reduces the load on thermal degasification and also the energy
consumption for the same.
VOLUME REDUCTION
Multi Effect Evaporator Once these two aspects are attained to, the evaporation to the desired degree becomes a simple physical operation and this can be done in a well designed Multi Effect Evaporator system
SECONDARY TREATMENT
1. Composting
Freezing of secondary / disposal technique still eludes
consensus and many distilleries have adopted composting as the
secondary / disposal technique. Forced by the limitations of
Pressmud and the land availability, an intermediate stage of R.O. /
M.E.E. was added. This technique however has the limitation of
limited period operation since composting cannot be carried out in
the rainy season. Non effective implementation of the composting
technology is also a problem observed at many distilleries. Also,
lately, the approving bodies/Committees have shown disinclination
towards Composting as a secondary technique due to
the above reasons.
2. Incineration Boiler
The technology of concentration followed by
incineration boiler is established at many a place. The initial
observations reveal the problems of serious effect on MOC used due
to high chloride contents and highly acidic input. This is besides the
extremely high capital costs of the project often surpassing the parent
industry establishment costs.
One more problem issue from working of this system is generation of ash, which contains the ash of secondary fuel – many a times coal,
there by containing heavy metals, thus making it non suitable for
agricultural purpose.
A new problem is faced in the context of change in working pattern, mainly use of main Raw Material used i.e. Mollasses, which is scarce and therefore is not sufficient for working of the distillery throughout the year and therefore, the industry has to use alternative raw material of Sugarcane Juice/syrup or B Heavy Mollasses for almost half the year. Since the wastewater (Spent wash) from this raw material use has far different characteristics, and which are not suitable for ‘Incineration Boiler’, many a distilleries, who have provided for this technology, are in a dilemma of not able to utilize their principal method of treatment for almost half the year. (Generally, season Months.)
A need is felt to develop a technology, which can work
throughout the year, (considering that the industry cannot afford to
close down for a yearly period of 90-100 days) and also to counter the
bad effect of particular weather at some sites having high humidity
contents. A judicious combination of established primary treatment
of Anaerobic Digester, which not only gives the desired output on
organic matter reduction front and also yields precious energy, and
which has been operative at many a distilleries is to be used as a first
stage.
Considering the overall aspect of non acceptability of composting as a
secondary / disposal technique, it is proposed to adopt an alternative
technology of ‘Drier mechanism’ which is approved as zero
discharge method by MoEF in addition to the Incineration Boiler
technology.
DRIER MECHANISM
Instead of utilizing the composting technique, which had
severe limitations as stated above, and was proving to be a
cumbersum operation, it is proposed to utilize a drier mechanism,
specially developed to convert this concentrated spentwash, along
with binder material into a powder, which is a non drip mass, which
constitutes mainly inorganic concentrations having fertilizer values
and organic carbon in a required tolerable limits for the soil
application.
Besides avoiding the tidious operation of composting, this method also
has advantage of avoiding pollution of ground water which many a
times resulted due to uncontrolled spraying of spentwash. As said
earlier, since this method is technically approved as zero discharge
method, the distillery can function throughout the year.
ORGANIC FERTILIZER
Realizing the importance of positive impacts of using organic fertilizers for the fields and to conserve and cash on the nutrient values gained from the powder from Dryer mechanism having high nutrient values, it is proposed to convert the same in organic manure/ soil conditioner by homogenizing with micronutrients, other soil conditioner ingredients in the required proportion.
ENERGY GENERATION
It is proposed to utilize the biogas produced from the Biodigester for conversion in high value CNG production by techniques of scrubbing and compression to high pressure. This alternative has got the highest payback potential for the biogas utilization mode.
CONDENSATE POLISHING AND REUSE
The condensate evolved from both M.E.E and Drier is proposed to be treated based on well established technology, which is working successfully in India and abroad for past few years. This will also contribute to considerable saving in the freshwater requirement of the distillery operations.
RECONNAISSANCE
It is intended to achieve zero discharge solution for the probleminous effluent from distillery industry by adopting proven treatment methods which are not only less cost intensive, have lower working problems, but also result in by products having substantial payback potential. The sub techniques are proven technologies based on years of experience in implementing the same, besides being low on capital and working cost requirement. This composite technology shall be the best techno-economic alternative for achieving Zero Discharge in a beneficial way, both for the industry and Environmental Conservation.
SCHEMATIC PROCESS FLOW DIAGRAM FOR EFFLUENT TREATMENT PLANT FOR DISTILLERY (ZERO DISCHARGE)

BIODIGESTER PROJECT AT SHRI CHH. SHAHU S.S.K. LTD.

DRIER SYSTEM

CONDENSATE POLISHING UNIT FOR DISTILLERY AT METAHARA SUGAR FACTORY, ETHIOPIA