Technical Note
CONDENSATE POLISHING UNIT FOR SUGAR FACTORY
Where in the Central Pollution Control Board vide their latest circular has made the Condensate Polishing and Reuse as a compulsory activity, it is extremely beneficial for the Karkhana to install such a system which optimizes the water use to a minimum.
Water is an important constituent of the manufacturing process in sugar factories and allied industries. With the growing scarcity of water, the emphasis is on conservation of this resource and recycle of the same to a maximum extent. Efforts were initiated long back to identify partially polluted or unpolluted sources of water, which can be recycled with partial / no treatment, to achieve minimum water consumption.
With this growing realization, the Industrial Management of Prominent Groups of Sugar Factories, with the advice from TechnoEnviron Consultants have taken initiatives in managing the available resources and achieving Total Water Management through resource conservation, reutilization, and recycling, wherein, it was possible to achieve “ZERO WATER INTAKE” practically to meet the process demand of Sugar Factory and Co-Generation Units. The technology for “Condensate Polishing” is now well established and patented.

Water in cane is the most reliable source, and the condensate gained is almost pure, except for a few impurities, which are required to be treated before the water is available as the alternative raw water source. The initial attempts were to cool this source and use the condensate as it is for various process applications. The utilization of this condensate as it is has however proven detrimental, because of trace organic matter and more particularly, due to the Ammonical nitrogen content. The presence of these impurities resulted in the development of algal growth, particularly in cooling circuits thereby causing clogging and thus decreasing the efficiency of the equipments.
The idea of utilizing excess condensate to fulfill water requirement is nothing new and the same was in practice, at same sugar factories, mainly for washing, cleaning purposes. As we are all aware, the excess condensate contains temp, and trace organics as two visible forms of impurities. This was mainly countered by cooling the same in cooling tower and spray tower.
On retention in a tank for longer period, however due to degradation of Organic matter, water turned blackish by purification.
More and more stringant quality requirement areas like makeup of cooling tower for Co‐gen, cooling circuits has forced a re‐thinking on treatment requirement of this water. This was further demanded by increased scarcity of water day by day.
On careful analysis and observations at various sugar factories, one more hidden fact came to the notice. A significant level of Ammonical Nitrogen is present in this condensate. Factories using this directly observed blocking of cooling Circuits, minor pipelines by algal formation due to Eutrophication caused by the Ammonical Nitrogen.
About 6 years ago, we evolved first of the response to the requirement in Renuka Sugar Group, where biological mode of treatment, in which we specialize in, was established and tested successfully for this condensate water. Reduction of organic matter to the levels desired was another plus point. As we all are aware, this water proved to be 100 times better due to its low TDS, low hardness than the fluctuating quality river water we were drawing, at a huge expense and totally replaced it.
Further improvements in the reaction kinetics, provision of tertiary treatment has enabled to add this water straight to water reservoir, where it has become possible to utilize for the critical purposes of make- up of Co‐Gen cooling tower, Fermenter addition for distillery.
This thus can totally satisfy the water demand of industrial process, both for sugar factory and distillery, except boiler feed water besides reducing unnecessary load on disposal system, which is proving to be troublesome for every sugar industry.
The positive effects observed for technology developed and monitored are reduction of scale formation in the pipeline circuits, cooling tower components, increase in efficiency of cooling due to low TDS, and above all non‐dependence on external water.
The Project is Cost Economically viable and also contributes greatly to the Conservation of Water Resource.
SCHEMATIC PROCESS FLOW DIAGRAM FOR CONDENSATE POLISHING UNIT FOR SUGAR FACTORY
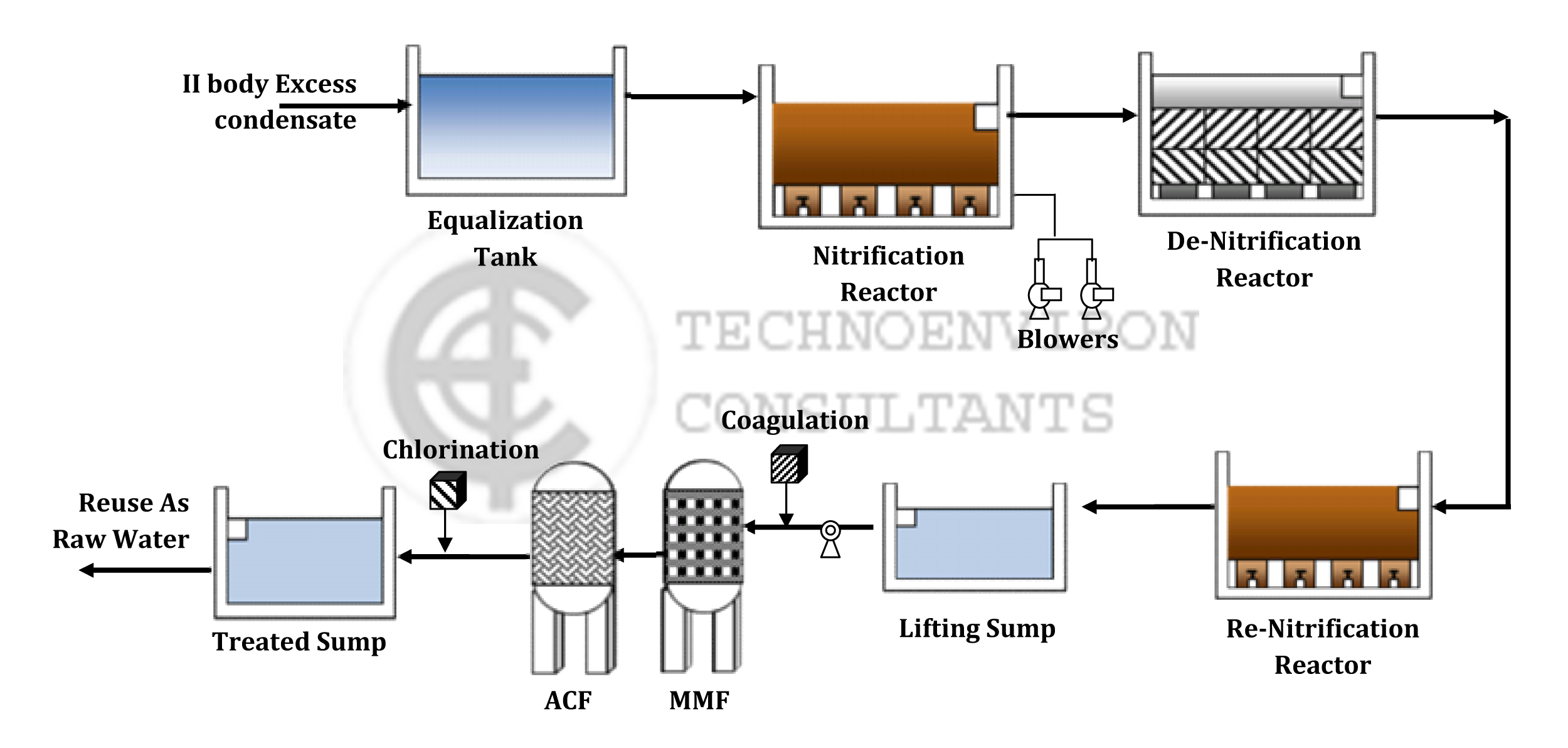
STAGES IN DEVELOPMENT OF TECHNOLOGY FOR CONDENSATE POLISHING
1) Direct Use in Processes
The initial attempts were to cool this source and use it as it is for various process applications. The presence of organic matter and more precisely ammonical nitrogen resulted in development of algal growth, particularly in cooling circuits and clogging the same. The efficiency of the equipments was greatly hindered. This necessitated a rethinking on the subject for treatment of these two impurities
2) Use of RO/Resin Beds as treatment technique
This was attempted at some sugar factories. However, since RO does not take care of the organic matter, the problems remained the same.
3) Treatment for Organic Matter
This treatment proved successful for reduction in organic matter content, but failed in terms of Ammonical Nitrogen removal, which was the main contributor to increase in Eutrophication.
4) Treatment for Ammonical Nitrogen
A specific biological treatment scheme was designed and tested successfully for reduction in ammonical nitrogen concentration. Reduction in organic matter is an added bonus.TREATMENT APPROACH
The major impurity contents of sugar factory condensate are trace organics and more particularly the Ammonical Nitrogen which can prove detrimental for reuse applications.
The treatment scheme for condensate polishing unit involves the utilization of biological mode, specially developed to treat not only trace organics, but basically the Ammonical nitrogen. The treatment scheme therefore comprises of an Aerobic – Anaerobic approach.
Although, the characteristics of condensate are fairly uniform with reference to period, it is desirable to provide some cushion for minor variations in the form of equalization tank. This also serves as a part of composite and complex biological system specially developed as the treatment scheme. The condensate is subjected to aerobic and anaerobic biological modes selectively to cater for and treat the two main impurities. Care is taken to optimize the treatment structures as well as the energy inputs, thereby minimizing the capital as well as working expenditures.
SALIENT ADVANTAGES OF USING TREATED CONDENSATE WATER SUBSTITUTING RAW WATER IN A SUGAR FACTORY COMPLEX
1) Cooling Tower Makeup- Co-Gen
Since there is a limit for TDS and hardness specified for the Co-Gen Cooling Tower water and the concentrations of both TDS and Hardness go on increasing due to cyclic rotation, it is necessary that water having low concentration of both the parameters replaces the loss of water due to windage and evaporation. The normal practice of using sand filter and in some cases the softener does remove the suspended solids and hardness but the TDS, which is a vital parameter for cooling efficiency remains unaffected. Addition of treated condensate helps in maintaining the desired levels, without drain off from cooling tower, which again adds to effluent load.
2) Cooling Circuits makeup
With the growing concentration of silica in the raw waters, and largely Non-reliable methods for removal of the same, large scale depositions are found lately in the cooling circuits, which use raw water. This is more detrimental, where there are small gap-critical cooling circuits like turbine sections. An off season maintenance seldom finds obstructive scales of silica, affecting the operation of these cooling circuits and many a times causing a serious failure, which proves costly. Use of treated condensate eliminates this possibility.
3) General Washing
Even for general washing purpose, since the raw water is required to be subjected to softener treatment, thereby removing the scale forming components, as otherwise this finds way into the machinery components, thereby limiting the efficiency. Use of Treated Condensate eliminates this possibility.
4) Fermenter Makeup for Distillery
Where there is an allied industry of distillery, the treated condensate (from Sugar) is found to be best replacement for raw water being used for fermenter make-up water. This also ensures that the fermenter make up water also has low TDS and hardness